VisionaryPoint.
What are the pillars of a solid corporate governance ?
Unlock GRC Series
Episode #02
Meaning and Definition of Governance in the Context of GRC.
What is the Meaning of Governance ?
In the context of Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC), governance refers to the processes, structures, and mechanisms put in place within an organization to oversee and control risk management and compliance with standards, regulations, and internal policies.
Understanding key objectives
Governance in the GRC framework typically involves defining the roles and responsibilities of stakeholders, including board members, management, compliance officers, and risk managers. It also entails establishing clear policies, procedures, and guidelines to guide activities related to risk management and compliance.
In this context, good GRC governance aims to ensure transparent, responsible, and effective decision-making regarding risk management and compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices. It also fosters a corporate culture focused on integrity, ethics, and accountability in all of the organization’s activities.
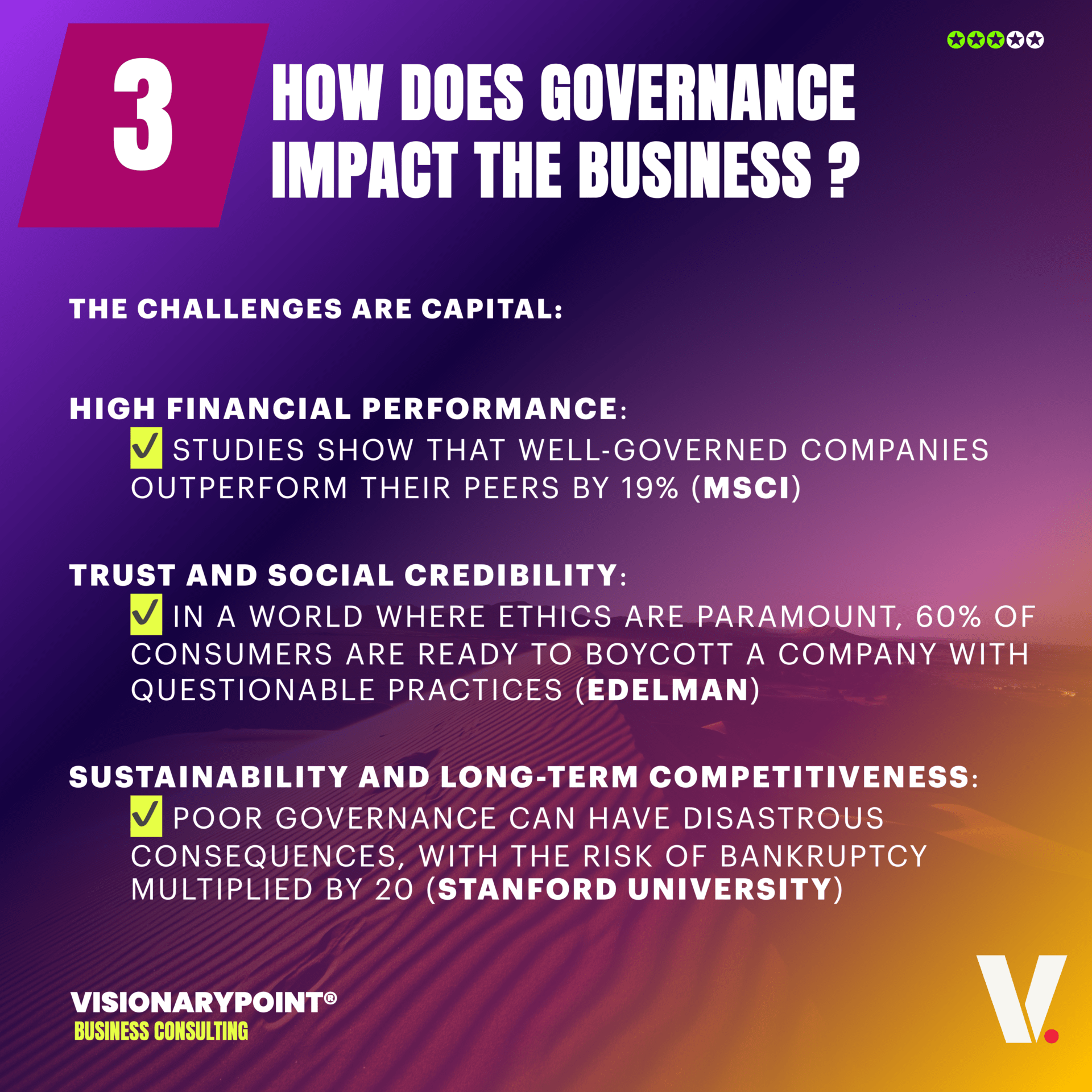
The pillars of a solid corporate governance
In the current context of uncertainties and unprecedented challenges, building a strong and effective corporate governance has become a major strategic imperative for any organization aiming to thrive sustainably. According to a recent study by the Risk Advisory Group, 83% of executives now consider GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) as a key lever for resilience and performance. Yet, according to the Gartner 2023 GRC maturity barometer, only 27% of large companies claim to have a truly robust and integrated risk governance framework. This substantial gap underscores the urgency to take action.
To address this, leading actors rely on five fundamental pillars, as illustrated by the inspiring examples below. Deployed coherently, these pillars transform GRC into a real differentiator, creating sustainable competitive advantages.
What are the pillars of Corporate Governance ?
The five pillars of Corporate Governance in the context of GRC enable companies to create an environment of effective control and risk management, thereby contributing to better decision-making, reduced losses, and increased shareholder value.
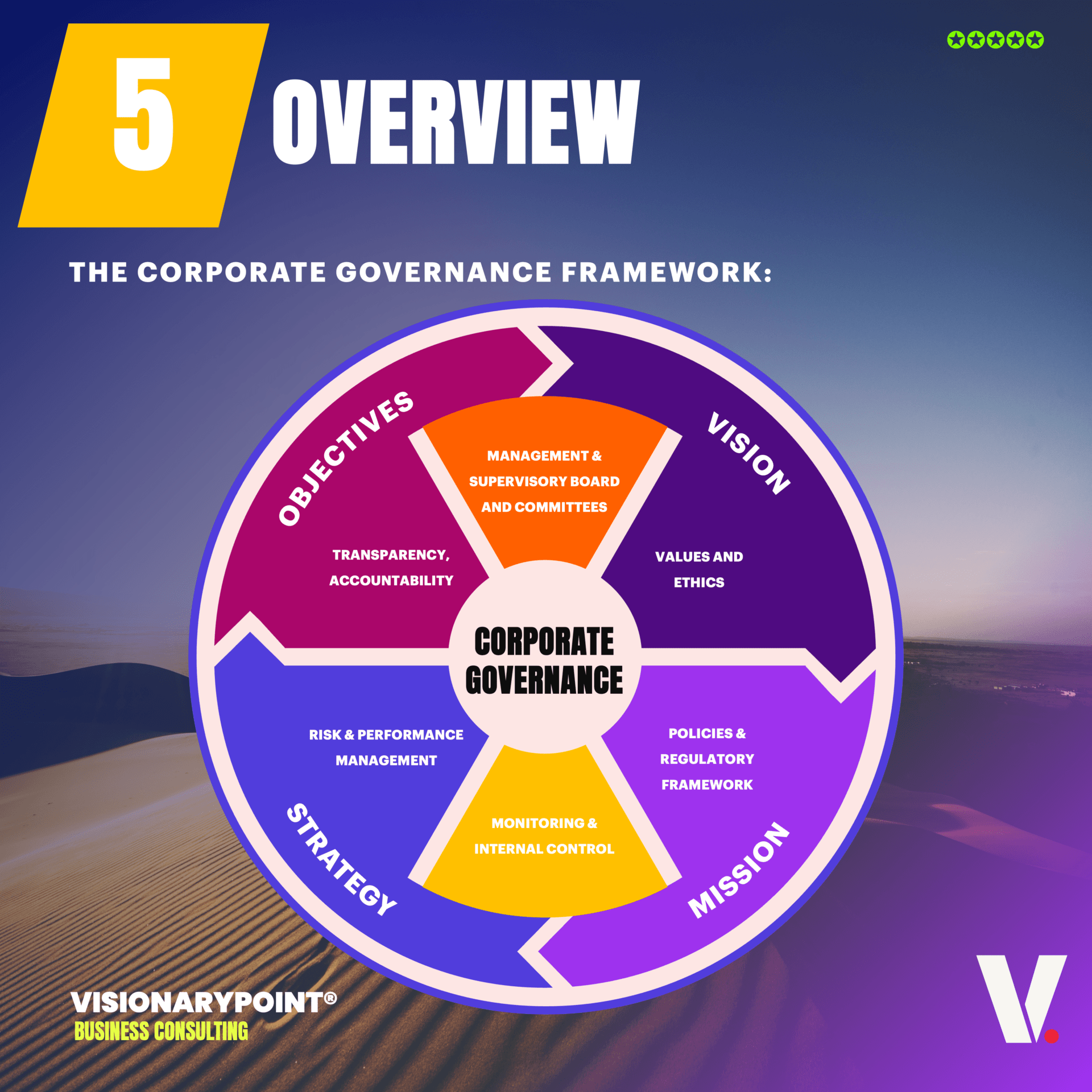
Let’s dive into the five pillars of Governance Framework :
Governance Framework

Strategic Benefits of GRC Implementation.
Implementing GRC offers strategic benefits for organizations. It enhances decision-making by providing a holistic view of governance, risk, and compliance factors. GRC implementation helps identify and manage risks more effectively, ensures compliance with regulations, and promotes a culture of transparency and accountability. Ultimately, it enables organizations to achieve operational efficiency, enhance stakeholder trust, and drive sustainable business growth.
Governance Structure.
Strong leadership and commitment at the highest level
At the heart of any risk governance lies the personal involvement of executives. At Anglo American, one of the world’s leading mining resource companies, the CEO himself chairs the Sustainability Risk Committee. A strong initiative that fully integrates the ESG dimension into the group’s strategic risk management and growth strategy.
Another telling example is Covéa Group (France’s leading property insurer), which has established a dedicated structure, the « Global Major Risk Governance, » directly reporting to the CEO. A clear signal that facilitated the deployment of an ambitious GRC policy across the company’s various business lines.
Strong leadership and commitment at the highest level rely on the belief that risk decisions cannot be taken lightly. Executives must not only be aware of the risks but also fully integrate them into their strategic vision. By adopting a proactive approach to risk management, leaders can not only anticipate potential challenges but also leverage emerging opportunities to drive growth and innovation.

Advice
Appoint a Chief Risk Officer (CRO)
Aligning GRC Vision Across Organizational Levels. A Strategic Imperative
It is therefore crucial for leaders to operationalize their GRC vision at all levels of the organization. This involves integrating GRC strategy into the corporate culture and developing detailed action plans for its implementation. Ongoing alignment between top management and frontline teams is essential to ensure effective implementation of the GRC strategy and ensure that objectives and actions are consistent at all levels.
Empowering GRC Leadership. The Role of the Chief Risk Officer (CRO)
The appointment of a senior-level Chief Risk Officer (CRO), directly reporting to the CEO, is essential to coordinate GRC initiatives across the organization. The CRO plays a key role in defining GRC strategy, managing risks, and communicating with internal and external stakeholders.
Comparing Two Pillars of Effective Governance
For real effectiveness, GRC cannot remain siloed. It must be part of a cross-functional governance integrating all relevant frameworks. A pioneer in this area, BNP Paribas has implemented a three-level integrated governance model: the board of directors and its specialized committees, executive bodies (risk and compliance committees at group/business levels), and dedicated functions.
Similarly, BASF, a global leader in chemistry, has chosen to unify its structures under a single entity, Corporate Risk Management, covering operational and financial risks, as well as internal control, compliance, and sustainable development. A holistic approach that has proven successful.
The importance of creating dedicated and integrated governance bodies means that risk management should not be treated in isolation but rather integrated into the overall governance processes of the company. By adopting a holistic approach, organizations can ensure effective coordination among various stakeholders and ensure informed decision-making.
The Three Lines Of Defense in GRC
It is crucial to emphasize the concept of the three lines of defense in GRC, with risk owners as the first line, compliance function as the second line of control, and internal audit as the third line providing an overall and independent view.
This approach ensures effective risk management and adequate oversight at all levels of the organization.

Advice
Establish Specialized Committees
Unified Strength
It is important to detail the various specialized committees that can be established, such as risk, audit, ethics committees, etc. Each committee should have a multidisciplinary composition, including members from legal, financial, CSR, etc., departments.
These committees play a crucial role in overseeing and managing risks within the company:
- Risk committee (controls, mapping, action plans)
- Audit committee (compliance, fraud, insurance)
- Ethics committee (ethics, CSR, compliance)
- Multidisciplinary composition including Legal, Financial, CSR …

Risk and Compliance Vision.
Beyond Governance
Beyond governance, cutting-edge GRC relies on a dynamic and integrated 360° mapping of risks/compliance. A complex challenge solved, for example, at Saudi Aramco through a GRC digital platform allowing consolidated and continuous visualization and management of all strategic, operational, financial, cyber, ESG risks, etc.
Chemical company Solvay offers another exemplary case with its « Permacarto » device. This system models emerging risks and their potential impact in real-time. An approach that allows the company to anticipate and constantly adjust its positioning and strategic trajectory.
Advice
Examples of Advanced AI Tools
Consolidated Vision
It is important to have a consolidated vision of risks and compliance. In a world where risks are increasingly interconnected and complex, it is essential to have tools and processes to map and prioritize risks dynamically. By adopting a proactive approach to risk management, organizations can not only anticipate potential challenges but also identify emerging opportunities and make informed decisions.
In this regard, concrete examples such as Allianz’s dynamic risk matrix, which allows real-time visualization of emerging threats, or Uber’s use of predictive AI to anticipate litigation and adjust its claims management policy, perfectly illustrate the importance of an innovative approach to risk management.
Advanced AI Tools
Concrete examples of advanced tools combining internal/external data, AI, and predictive modeling, such as the FourTwentySeven solutions used by major corporations, illustrate the importance of technological innovation in risk management. These tools enable companies to better anticipate emerging risks and make real-time decisions.
Risk, Ethics, and Compliance Culture.
But sustainable performance requires more than just a technical device, however robust it may be. Because GRC is only valuable with the adherence and commitment of all employees.
In this perspective, Volvo Group relies on its « Serbia Remos » program to continuously develop teams’ skills in risk management. Dedicated training paths, assistance in deploying methodological tools, field support for risk functions: all levers are activated to gradually anchor a conducive managerial culture.
Commodity trader Trafigura has also made GRC a major focus of its cultural transformation, integrating its new CSR principles (human rights, environment, ethics, etc.) extensively. A drastic change for this company long criticized.
Advice
Engaging Awareness Initiatives
Cultivate a risk management culture
It is important to cultivate a risk management culture within the organization. This means that risk management should not be perceived as the exclusive responsibility of specialized departments but rather as a shared responsibility among all employees. By encouraging a culture of transparency, openness, and accountability, organizations can create an environment conducive to the identification and proactive management of risks.
In addition to training, it is essential to establish risk culture measurement barometers with employees. Also, value whistleblowers who can detect potential flaws in the company’s processes or practices early on, thus strengthening a culture of transparency and openness.
Involve all employees in the GRC process
It is also important to describe engaging awareness initiatives, such as serious games and interactive MOOCs, to involve all employees in the GRC process. These innovative approaches make risk training and awareness more attractive and accessible at all levels of the organization.
Effective Internal Control.
Internal control refers to the processes, policies, and mechanisms established by an organization to ensure the reliability of financial reporting, protect the company’s assets, and comply with established policies and procedures.
Here are some key elements of this pillar:
Internal Control
Processes and Procedures
Organizations must have well-defined processes and procedures for all key activities, including financial management, business operations, and regulatory compliance. These processes must be documented and regularly reviewed to ensure their effectiveness and relevance.
Establish Controls Points
Internal controls are the policies, practices, and mechanisms put in place to ensure that the organization’s activities comply with established standards and regulatory requirements. This may include IT controls, physical security controls, authorizations and approvals, as well as monitoring and verification processes.
Separation of Duties
To reduce the risks of fraud and errors, it is essential to have adequate separation of duties within the organization. This means that different individuals or teams are responsible for different steps in a process, limiting opportunities for collusion or manipulation of activities.
Supervision and Monitoring
Regular monitoring is necessary to ensure that internal controls are functioning as intended and to identify gaps or potential weaknesses in processes. This may involve periodic reviews by management, internal or external audits, and mechanisms for reporting violations or irregularities.
Culture of Accountability
Finally, an organizational culture that values responsibility, integrity, and ethics is essential to support effective internal control. Employees should be encouraged to report potential issues and to adhere to established policies and procedures to ensure compliance and transparency.
Internal control aims to ensure that the organization’s activities are managed in a responsible, transparent, and compliant manner, reducing operational, financial, and compliance risks.
Advice
Harnessing AI Potential
Enhanced Risk Management
The potential of AI to automate certain key controls or proactively detect sophisticated fraud is an important aspect to highlight. Advances in AI enable companies to strengthen their ability to identify and mitigate risks while improving the efficiency and effectiveness of control processes.
Also, leveraging data and artificial intelligence to boost risk analysis and decision-making. A strategic asset seized by leaders as they climb the « data-driven » maturity ladder.
This was reflected at CapGemini by the deployment of a « Risk Intelligence Factory » combining advanced data mining, predictive analysis, and real-time monitoring solutions. Powerful tools to optimize risk governance across the entire group’s ecosystem. In the same vein, Rio Tinto has launched its ambitious « Data Integrated Risk Vision » program. Its goal? To leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to dynamically model all scenarios of operational, financial, geopolitical risks, etc. to more effectively inform strategic decision-making.
Harnessing the potential of data to optimize risk management is relevant for several reasons. First, in an increasingly data-driven world, organizations have a treasure trove of information that can inform risk decision-making. Second, by adopting a data-driven approach, organizations can not only enhance their ability to identify and assess risks but also anticipate emerging trends and make strategic decisions.
AI can also be used to promote business ethics and social responsibility by automatically detecting on social media statements that contradict the company’s ethics. This allows organizations to quickly respond to potentially harmful situations and enhance their reputation and credibility.
Communication and Transparency.
It is essential to communicate clearly and concisely with internal and external stakeholders regarding GRC-related activities and initiatives. For example, BMW regularly organizes information sessions for its employees to raise awareness about GRC issues and gather their feedback.
Publishing transparent reports demonstrates commitment to transparency and accountability. In this regard, TotalEnergies annually publishes a detailed report on its risk management policy and internal control system, audited by an external firm.
Engaging stakeholders strengthens the effectiveness and legitimacy of governance processes. SNCF has set up an « ethics and CSR committee » composed of representatives from customers, suppliers, and NGOs to identify non-financial issues and co-design its action plans.
It is also important to ensure transparency with shareholders, as L’Oréal does by presenting annually to the board of directors a comprehensive report on the assessment and treatment of key emerging risks.
Constructive exchanges with regulators, like those organized by Crédit Agricole, help proactively evolve the internal control system. Finally, Michelin surveys NGOs, directors, and analysts about their perception of its CSR risk management.
In three key steps, here’s what we recommend :
Communication and Transparency Guidelines
Effective Communication with Stakeholders
It is essential to communicate clearly and concisely with internal and external stakeholders regarding GRC-related activities and initiatives. This includes disseminating information about policies, procedures, internal controls, and the results of risk assessments.
Publication of Transparent Reports
Publishing periodic reports on risks, internal controls, and the culture of ethics and compliance of the company demonstrates commitment to transparency and accountability. These reports provide important information to stakeholders about how the organization manages risks and complies with standards and regulations.
Collaboration with Stakeholders
Actively involving stakeholders in identifying and managing risks and opportunities related to GRC strengthens the effectiveness and legitimacy of governance processes. This may include consultations with shareholders, employees, regulators, and other stakeholders to understand their concerns and perspectives.
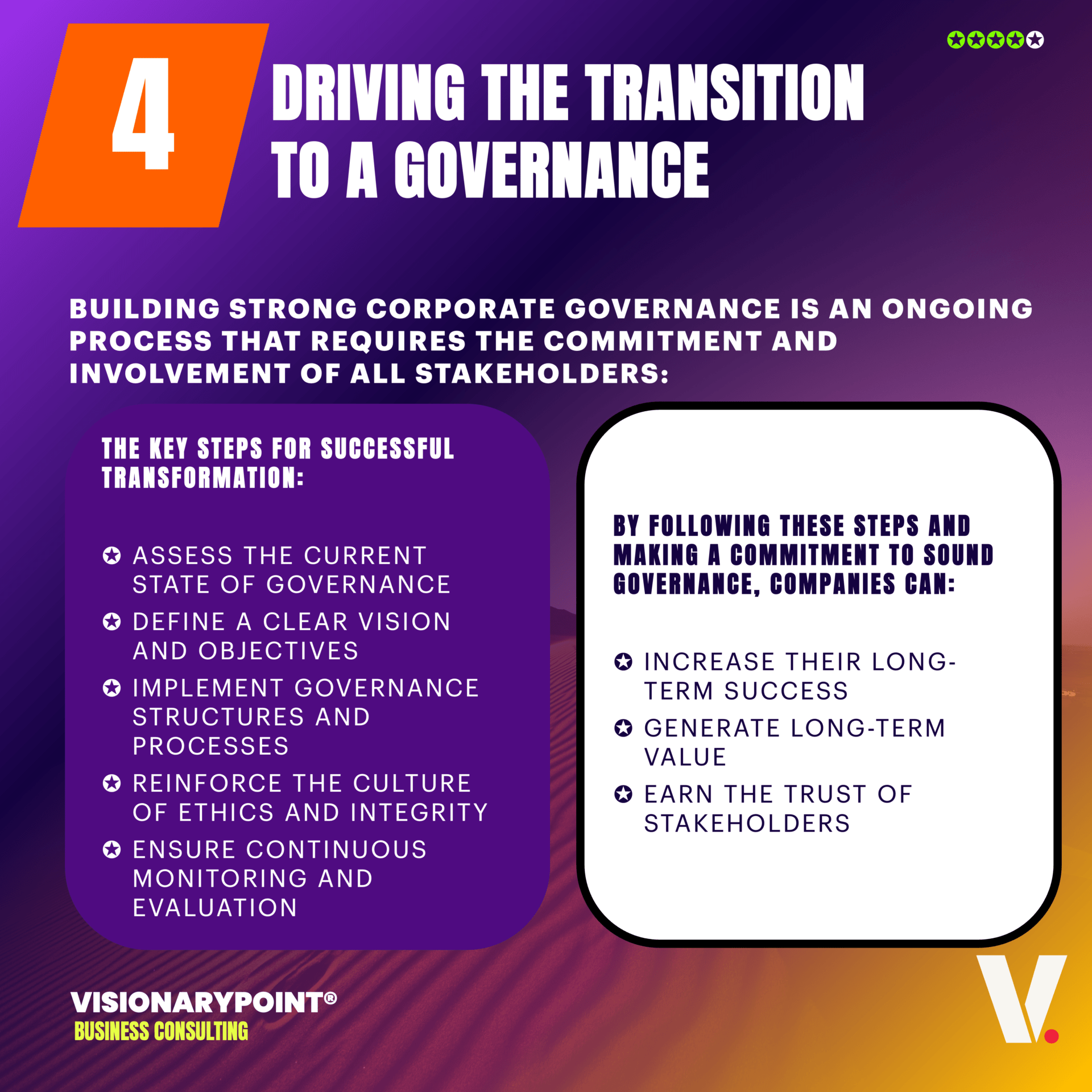
Conclusion
Risk Governance, a Strategic Imperative in a BANI World.
Risks today are more interconnected, dynamic, and difficult to anticipate than ever before. A simple localized disruption can quickly spread globally and impact multiple areas: financial, operational, reputational, cyber, etc. The COVID-19 pandemic is a perfect illustration, revealing many flaws in companies’ risk management systems, caught off guard by a systemic risk of such magnitude.
In this highly disruptive context, only the most agile and resilient organizations, which have made ERG a real competitive advantage, succeed in standing out. These pioneers have transformed their approach to risk governance by actively involving their top management, integrating agile processes into all their strategic and operational processes, and harnessing the full potential of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence. We’ll see more about this in an upcoming episode of Unlock GRC.