VisionaryPoint.
What is Governance Risk and Compliance ?
Unlock GRC Series
Episode #01
GRC meaning and definition.
What is the Meaning of GRC ?
The term GRC stands for governance, risk, and compliance, which was coined by OCEG and introduced officially in 2007 with the publication of the first peer-reviewed academic paper on the subject by OCEG founder, Scott Mitchell, in the International Journal of Disclosure and Governance. Although formalized in 2007, the concept of GRC has been prevalent for a considerable duration. Organizations have long recognized the significance of governance, and teams have incorporated risk management and compliance management programs into their business strategies for years.
Understanding the Principled Performance
Principled Performance of GRC aims to drive organizational success by promoting a culture of integrity, effective risk mitigation, and adherence to regulatory requirements. It allows organizations to optimize performance, enhance decision-making, and build trust among stakeholders.
In essence, GRC aims to empower stakeholders for well-informed decision-making. The strategic emphasis on advancing GRC and seamlessly integrating the practices of governance, risk, and compliance has grown in significance, especially with the escalating risks that bring heightened uncertainty and complexity.
The essence of Governance Risk and Compliance
GRC primarily aims to protect the organization against various risks – financial, reputational, operational, and so on. It is also about ensuring the company operates in a transparent and accountable manner towards its stakeholders.
Beyond these aspects of protection and transparency, GRC aims to promote ethical conduct and integrity throughout the organization. This notably involves reducing the risks of non-compliance with regulations and other legal requirements, which can result in costly fines or other sanctions.
In a broader vision, GRC seeks to improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the company’s operations. It is a holistic approach that aligns the strategy, operational processes, and compliance efforts, in order to optimize performance, better manage risks, and preserve stakeholder trust in the long term.
What is GRC ?
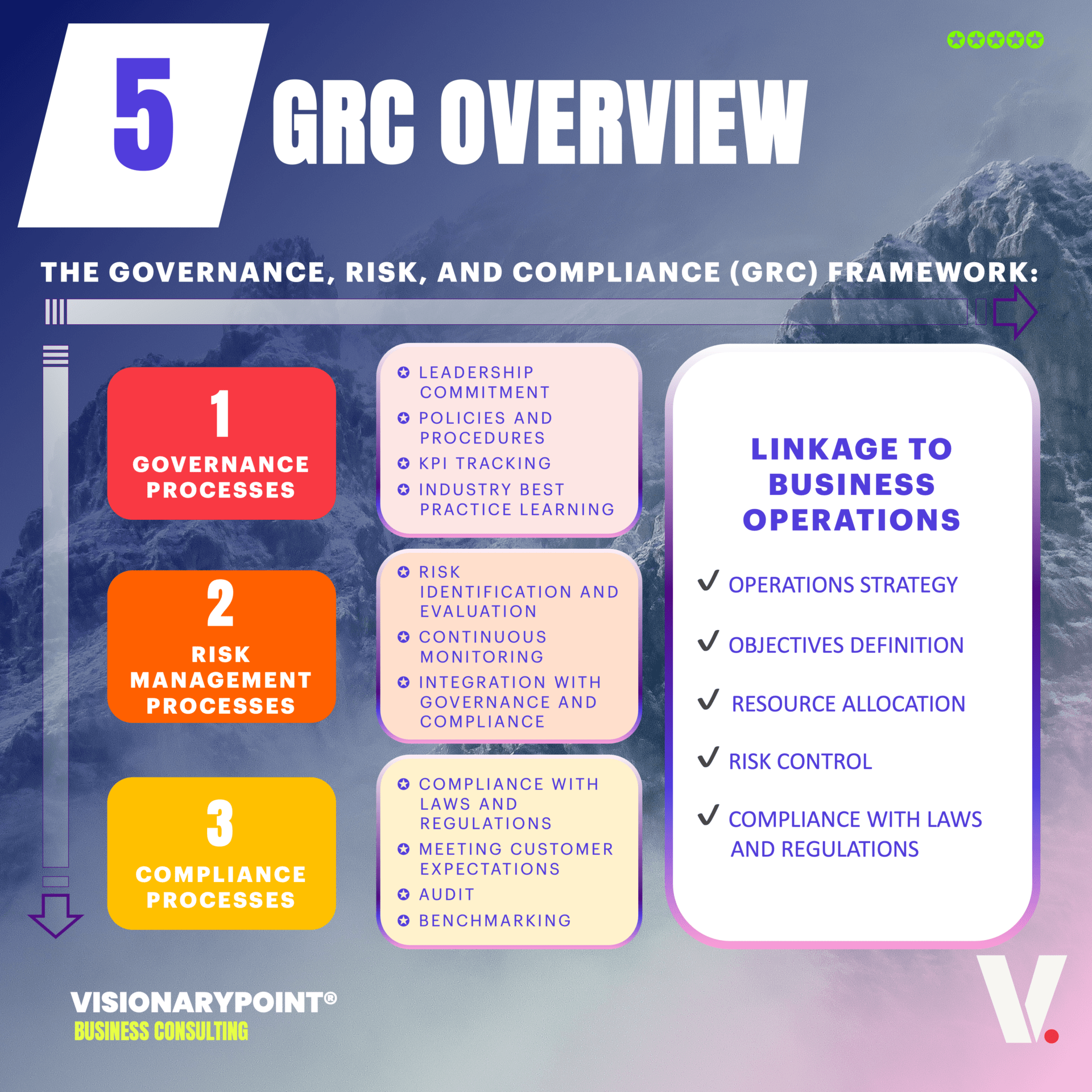
Governance, risk, and compliance represent a systematic approach that assists organizations in complying with industry and government regulations, navigating risks, and attaining business goals. A holistic GRC strategy incorporates a blend of people, processes, and technology. Ultimately, proficient GRC management facilitates the dismantling of organizational silos, promotes operational efficiency, and empowers leaders to make quicker decisions.
Let’s dive into the goal of each GRC practice area :
Governance in Every Decision.
Governance involves decision-making and strategic direction, ensuring consistent and effective leadership to achieve organizational objectives.
Risk in Uncertainty.
Risk encompasses uncertainty and the possibility of adverse events that could negatively impact organizational objectives. Risk management aims to identify, assess, and mitigate these uncertainties.
Compliance in Every Action.
Compliance is about adhering to laws, regulations, standards, and relevant policies. Effective compliance management ensures that the organization’s actions align with current legal and regulatory requirements.
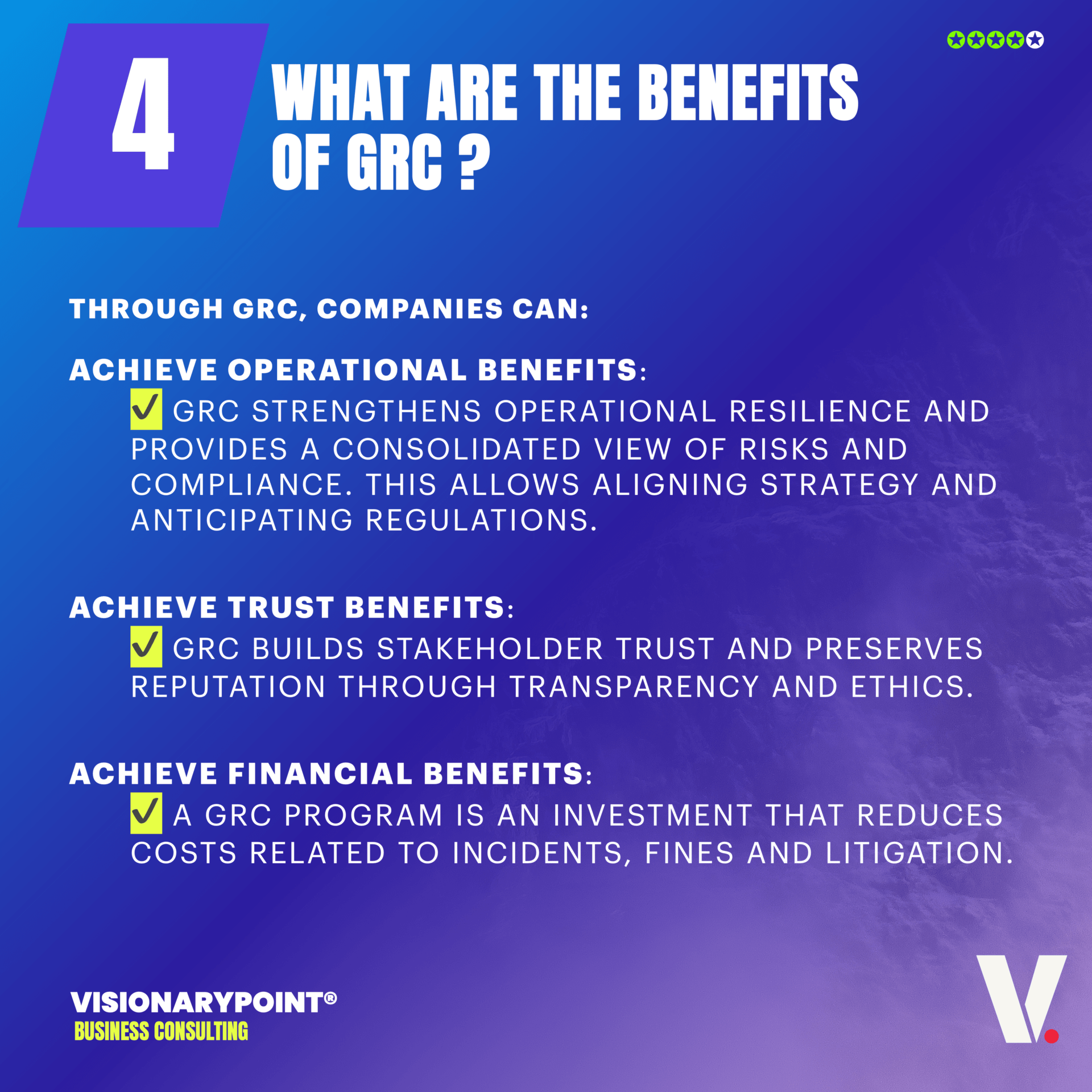
Strategic Benefits of GRC Implementation.
Implementing GRC offers strategic benefits for organizations. It enhances decision-making by providing a holistic view of governance, risk, and compliance factors. GRC implementation helps identify and manage risks more effectively, ensures compliance with regulations, and promotes a culture of transparency and accountability. Ultimately, it enables organizations to achieve operational efficiency, enhance stakeholder trust, and drive sustainable business growth.
Compliance vs. governance.
Strategic Alignment. Where Compliance and Governance Converge
Compliance and governance, though distinct, share a vital connection. Compliance involves adhering to external regulations and standards to prevent legal violations, while governance is the overarching framework guiding an organization’s operations. Governance sets rules and practices, defining roles and fostering accountability and transparency. Compliance, a subset of governance, specifically addresses regulatory adherence, with both working in tandem to ensure ethical operations aligned with strategic goals. Strong governance forms the basis for effective compliance, ensuring comprehensive ethical standards throughout an organization.


Compliance vs. risk management.
Comparing Two Pillars of Effective Governance
Compliance and risk management are two essential components of an organization’s governance framework, but they serve distinct purposes.
Risk management, is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could impact an organization’s objectives. It involves identifying potential risks, evaluating their likelihood and potential impact, and implementing strategies to minimize or eliminate those risks.
While compliance aims to ensure adherence to external requirements, risk management aims to identify and manage internal and external risks that could affect an organization’s performance and objectives.
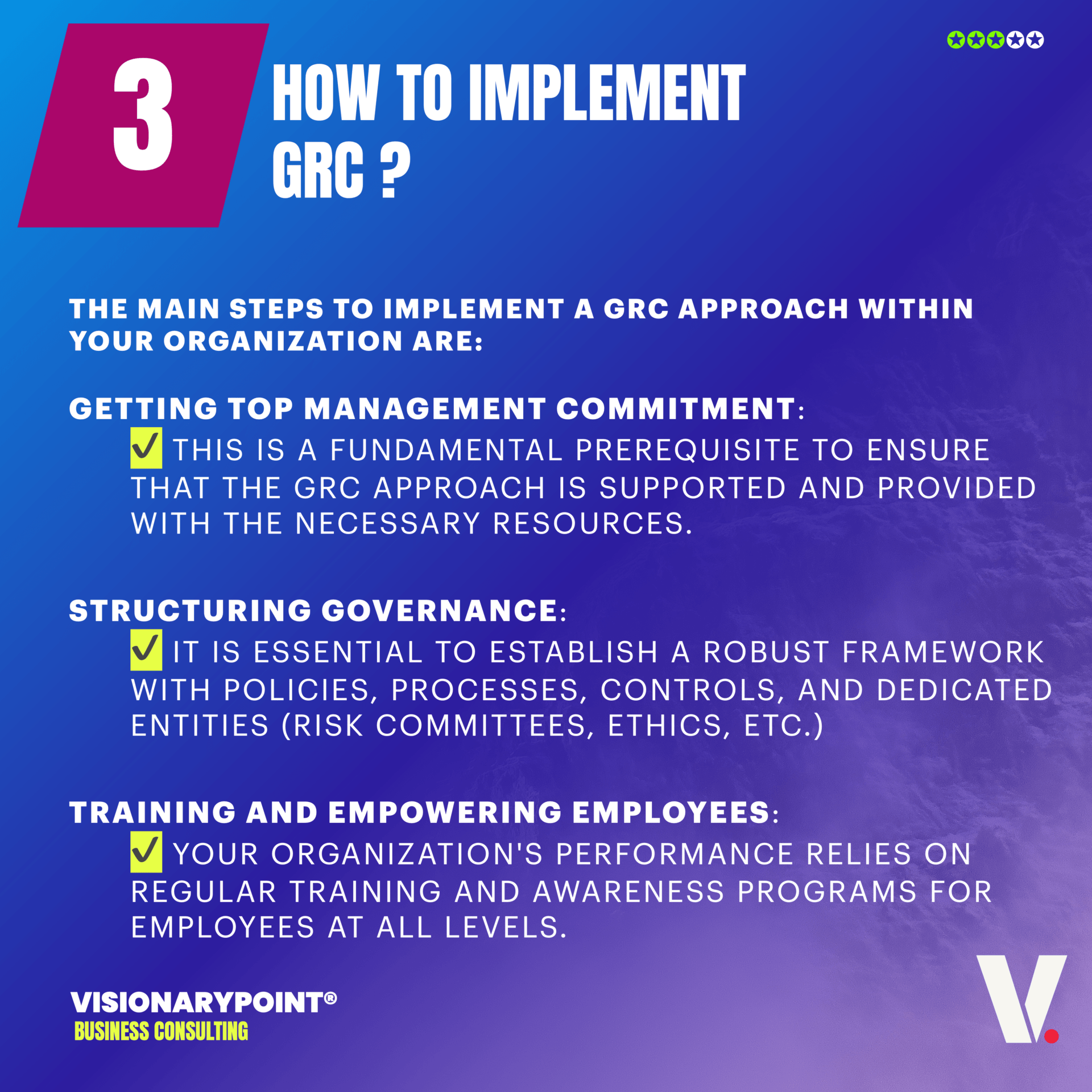
What is a GRC framework ?
A GRC framework serves as a structured and systematic model to manage governance, risk, and compliance processes within an organization. It provides a set of guidelines and best practices to help organizations establish effective policies and procedures that minimize potential risks and ensure regulatory compliance. By implementing a GRC framework, organizations can create a cohesive structure for managing and integrating governance, risk management, and compliance activities.
Some commonly used GRC frameworks include COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission), COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies), and ISO 27001 (International Organization for Standardization). These frameworks offer predefined frameworks, principles, and controls that organizations can adopt and tailor to their specific needs.
By adopting a GRC framework, organizations can enhance their ability to identify, assess, and manage risks, ensure compliance with applicable regulations, and ultimately achieve their goals while maintaining strong governance practices.
GRC teams and skills
GRC Team’s Function
Unified Strength
While a dedicated GRC team might not be a standard feature in most organizations, various stakeholders from diverse departments actively engage in governance, risk management, and compliance. This entails extensive collaboration among multiple teams, encompassing the board of directors, executive management, internal audit, risk, finance, legal, IT, security, compliance, strategy, HR, and more.
Building Successful GRC through Team Collaboration
The specific teams involved may vary based on the organization’s size and structure, but achieving alignment across these teams is crucial for establishing a successful GRC program. Whether it’s the board, executive leaders, or various departments contributing to GRC, breaking down silos and facilitating real-time collaboration is imperative to effectively navigate risks in today’s intricate and rapidly evolving business landscape.
Essential Skills
Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and navigating industry-specific regulations and compliance standards.
Risk Assessment
Proficiency in identifying, evaluating, and mitigating potential risks to the organization..
Data Analysis
Analytical skills to interpret complex data and extract meaningful insights for decision-making.
Communication
Clear and effective communication to convey GRC policies and requirements to various stakeholders.
Legal Knowledge
Knowledge of relevant laws impacting the organization’s operations.
Ethical Decision-Making
Ability to make ethical decisions in challenging situations.
Strategic Alignment
Aligning GRC efforts with organizational goals and strategies.
Technology Competence
Familiarity with GRC tools, data analytics, and technology solutions.
Project Management
Overseeing GRC initiatives efficiently and ensuring successful implementation.
Collaboration
Working collaboratively with diverse teams and stakeholders for effective GRC integration.
GRC tools and technology
GRC Tools and Platforms
GRC Tools
GRC stands for Governance, Risk, and Compliance. GRC tools are software applications designed to help organizations manage and optimize their GRC processes. These tools typically include features such as risk assessment, policy management, regulatory compliance, and audit management.
GRC Platform
A GRC platform, on the other hand, refers to a more comprehensive and integrated software solution that brings together multiple GRC tools into a centralized system. It provides a common framework for managing governance, risk, and compliance activities across different functions and departments within an organization.
Difference
The main difference lies in the scope and integration of functionalities. GRC tools are individual software applications that address specific aspects of governance, risk, or compliance. In contrast, a GRC platform is a more encompassing solution that integrates multiple tools into a unified framework. While GRC tools may focus on specific areas such as risk assessment or compliance tracking, a GRC platform aims to provide a centralized and interconnected system for managing all aspects of GRC within an organization.
GRC Technology
Define your organization’s GRC needs
Clearly identify your organization’s specific governance, risk, and compliance requirements. Consider factors such as industry regulations, risk appetite, organizational structure, and existing GRC processes.
Identify key features
Create a list of essential features and functionality you require in a GRC solution. This might include risk assessment tools, policy management, compliance monitoring, incident management, reporting capabilities, and integration capabilities with existing systems.
Evaluate vendor reputation and experience
Research and evaluate potential GRC solution providers. Consider their track record, reputation, industry recognition, and customer reviews. Look for vendors with experience in your industry or similar organizations.
Consider implementation and usability
Determine the ease of implementation and usability of the GRC technology. Evaluate factors such as user interface, customization options, training and support provided by vendors, and the overall user experience. Consider if the solution can be easily adopted by your organization without major disruptions
Assess scalability and flexibility
Consider the ability of the GRC technology to scale and adapt to your organization’s changing needs. Verify if the solution can accommodate growth, handle increasing data volumes, and integrate with other systems and third-party applications.
Review security and compliance features
Evaluate the security measures and compliance features offered by the GRC technology. Look for features such as access controls, encryption, data privacy, audit trails, and compliance templates that align with your organization’s regulatory requirements.
Cost and ROI analysis
Assess the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, maintenance, and support. Consider the return on investment (ROI) of the GRC technology by analyzing its potential to streamline processes, reduce risks, improve compliance, and enhance overall efficiency.
Why does GRC matter for ESG ?
It is highly likely that your organization has initiated discussions or implemented an ESG reporting program. Given the dynamic landscape of regulatory requirements globally, including the introduction of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), numerous organizations are seeking to streamline the assurance process for both financial and non-financial reporting. This is in line with the objective of enhancing transparency and accountability in corporate sustainability practices.GRC tools and technology
To effectively support organizations in achieving their ESG goals, it is crucial to establish proper governance over ESG initiatives. While the « G » in ESG already denotes governance, this aspect specifically focuses on establishing a governance framework for your organization’s ESG strategy.
Consider the following key considerations and questions :
A Governance for ESG Success
Involvement
Which stakeholders and departments should be involved in your ESG program? Determine the key participants who will contribute to the development and execution of your organization’s ESG initiatives. This may involve representatives from sustainability, finance, legal, human resources, and other relevant areas.
Policy Definition
How will your organization define ESG policies? Establish clear policies that outline your approach to environmental management, social impact, diversity and inclusion, and corporate governance. Ensure that these policies align with industry standards and best practices.
Target Setting
What process will your organization follow to set ESG targets? Develop a structured approach to set measurable and time-bound ESG targets that are aligned with your overall strategy. Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) and establish a mechanism to regularly assess progress against these targets.
Roles and Responsibilities
Do you have the appropriate roles, responsibilities, organizational structure, and processes in place to support ESG and manage associated risks? Evaluate your organizational structure to identify any gaps related to ESG management. Assign clear ownership of ESG initiatives and establish effective communication channels to ensure accountability and oversight.
Stakeholder Communication
How will stakeholders regularly communicate and measure progress toward ESG goals? Establish mechanisms for ongoing communication and reporting with internal and external stakeholders. This includes sharing updates on ESG performance, seeking feedback, and addressing concerns or inquiries. Transparency and accountability are key.
Compliance with CSRD
If your organization needs to comply with the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), how will you prepare for the new requirements? Stay informed about the reporting obligations outlined in the CSRD, identify the necessary data collection processes, implement appropriate reporting procedures, and ensure compliance with the new regulations.
Key Steps for Internal Audit in ESG Reporting Assurance
Internal audit teams should familiarize themselves with prevalent ESG risks, assess their organization’s current ESG posture, include ESG risks in their overall risk assessment, audit the completeness and accuracy of ESG metrics and data, identify applicable regulations or standards, apply practices from financial reporting controls to sustainability reporting controls, and use COSO’s guidance and ICIF-2013 framework to establish effective controls for ESG reporting.
What is the role of GRC in cybersecurity?
The role of Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) in cybersecurity is crucial for establishing effective security measures and ensuring compliance with regulations and standards.
Here are some key aspects of GRC in cybersecurity :
Cybersecurity and GRC
Governance
GRC helps establish a framework for decision-making, accountability, and oversight in cybersecurity. It involves defining roles, responsibilities, and processes to ensure that cybersecurity initiatives align with business objectives and are effectively managed.
Risk Management
GRC plays a significant role in identifying and assessing cybersecurity risks. It involves conducting risk assessments, establishing risk appetite, and implementing risk mitigation strategies to protect critical systems, data, and infrastructure from cyber threats.
Compliance
GRC ensures adherence to applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards related to cybersecurity. It involves developing policies and procedures, implementing controls, and conducting regular audits and assessments to verify compliance and address any gaps or vulnerabilities.
Incident Response and Management
GRC frameworks include establishing incident response plans and procedures to effectively respond to and mitigate cybersecurity incidents. This includes identifying, containing, and remediating security breaches, as well as conducting post-incident analysis and implementing corrective measures.
Training and Awareness
GRC emphasizes the importance of cybersecurity awareness and training programs for employees. This helps in building a security-conscious culture, educating individuals about their roles and responsibilities in protecting sensitive information, and promoting good cybersecurity practices across the organization.
Ongoing Monitoring and Auditing
GRC ensures continuous monitoring of cybersecurity controls, processes, and systems to detect any anomalies or potential vulnerabilities. Regular audits and assessments help identify weaknesses and measure the effectiveness of security measures, enabling timely remediation and improvement.
CONCLUSION
GRC and ESG. Building Resilient and Sustainable Organizations.
Adopting a comprehensive GRC approach is vital for organizations to effectively manage governance, risk, compliance, and ESG factors. By designing a GRC strategy that aligns with business priorities, organizations can enhance their risk management practices, ensure regulatory compliance, and address key ESG considerations. Flexibility and the ability to adapt to changes are crucial for successful GRC management in the dynamic landscape of ESG requirements. By embracing a robust GRC framework, organizations can increase their GRC maturity, strengthen their sustainability practices, and demonstrate their commitment to responsible business operations.